CADC
This topic describes how to manage the “CADC” dataset.
“CADC” is a fusion dataset with 8 sensors including 7 cameras and 1 lidar
, and has Box3D type of labels on the point cloud data.
(Fig. 8).
See this page for more details about this dataset.
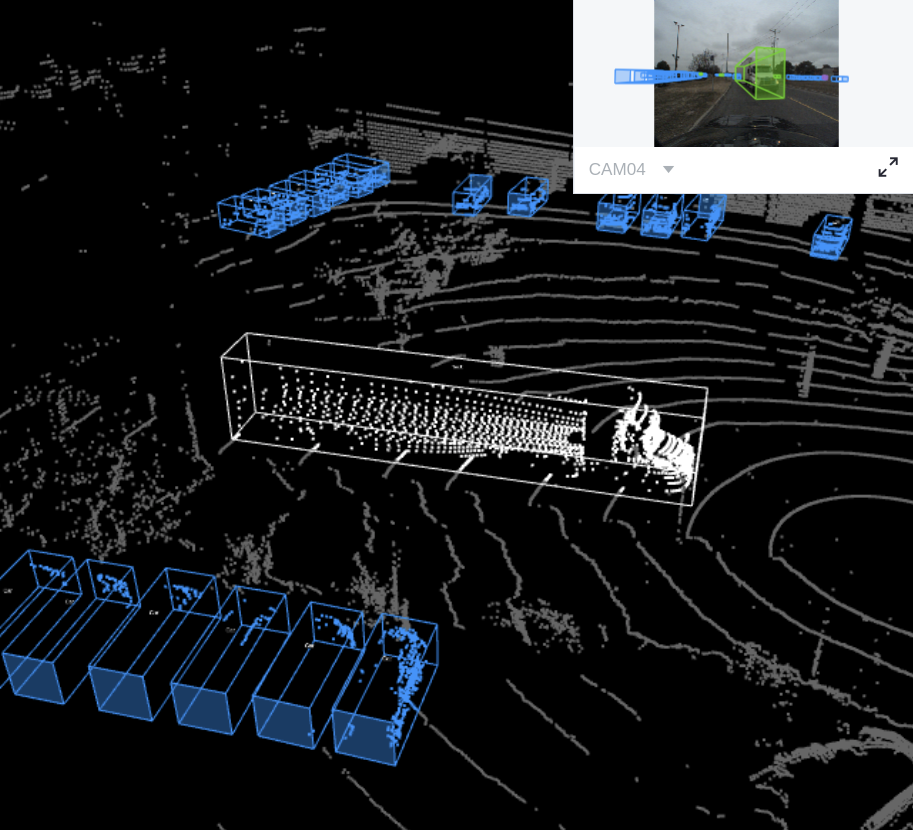
Fig. 8 The preview of a point cloud from “CADC” with Box3D labels.
Create Fusion Dataset
Then, create a fusion dataset client by passing the fusion dataset name and is_fusion argument to the GAS client.
gas.create_dataset("CADC", is_fusion=True)
List Dataset Names
To check if you have created “CADC” fusion dataset, you can list all your available datasets. See this page for details.
The datasets listed here include both datasets and fusion datasets.
gas.list_dataset_names()
Organize Fusion Dataset
Now we describe how to organize the “CADC” fusion dataset by the FusionDataset
instance before uploading it to TensorBay. It takes the following steps to organize “CADC”.
Write the Catalog
The first step is to write the catalog. Catalog is a json file contains all label information of one dataset. See this page for more details. The only annotation type for “CADC” is Box3D, and there are 10 category types and 9 attributes types.
1{
2 "BOX3D": {
3 "isTracking": true,
4 "categories": [
5 { "name": "Animal" },
6 { "name": "Bicycle" },
7 { "name": "Bus" },
8 { "name": "Car" },
9 { "name": "Garbage_Container_on_Wheels" },
10 { "name": "Pedestrian" },
11 { "name": "Pedestrian_With_Object" },
12 { "name": "Traffic_Guidance_Objects" },
13 { "name": "Truck" },
14 { "name": "Horse and Buggy" }
15 ],
16 "attributes": [
17 {
18 "name": "stationary",
19 "type": "boolean"
20 },
21 {
22 "name": "camera_used",
23 "enum": [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, null]
24 },
25 {
26 "name": "state",
27 "enum": ["Moving", "Parked", "Stopped"],
28 "parentCategories": ["Car", "Truck", "Bus", "Bicycle", "Horse_and_Buggy"]
29 },
30 {
31 "name": "truck_type",
32 "enum": [
33 "Construction_Truck",
34 "Emergency_Truck",
35 "Garbage_Truck",
36 "Pickup_Truck",
37 "Semi_Truck",
38 "Snowplow_Truck"
39 ],
40 "parentCategories": ["Truck"]
41 },
42 {
43 "name": "bus_type",
44 "enum": ["Coach_Bus", "Transit_Bus", "Standard_School_Bus", "Van_School_Bus"],
45 "parentCategories": ["Bus"]
46 },
47 {
48 "name": "age",
49 "enum": ["Adult", "Child"],
50 "parentCategories": ["Pedestrian", "Pedestrian_With_Object"]
51 },
52 {
53 "name": "traffic_guidance_type",
54 "enum": ["Permanent", "Moveable"],
55 "parentCategories": ["Traffic_Guidance_Objects"]
56 },
57 {
58 "name": "rider_state",
59 "enum": ["With_Rider", "Without_Rider"],
60 "parentCategories": ["Bicycle"]
61 },
62 {
63 "name": "points_count",
64 "type": "integer",
65 "minimum": 0
66 }
67 ]
68 }
69}
Note
The annotations for “CADC” have tracking information, hence the value of isTracking should be set as True.
Write the Dataloader
The second step is to write the dataloader.
The dataloader function of “CADC” is to manage all the files and annotations of “CADC” into a
FusionDataset instance.
The code block below displays the “CADC” dataloader.
1#!/usr/bin/env python3
2#
3# Copyright 2021 Graviti. Licensed under MIT License.
4#
5# pylint: disable=invalid-name
6# pylint: disable=missing-module-docstring
7
8import json
9import os
10from datetime import datetime
11from typing import Any, Dict, List
12
13import quaternion
14
15from ...dataset import Data, Frame, FusionDataset
16from ...exception import ModuleImportError
17from ...label import LabeledBox3D
18from ...sensor import Camera, Lidar, Sensors
19from .._utility import glob
20
21DATASET_NAME = "CADC"
22
23
24def CADC(path: str) -> FusionDataset:
25 """Dataloader of the `CADC`_ dataset.
26
27 .. _CADC: http://cadcd.uwaterloo.ca/index.html
28
29 The file structure should be like::
30
31 <path>
32 2018_03_06/
33 0001/
34 3d_ann.json
35 labeled/
36 image_00/
37 data/
38 0000000000.png
39 0000000001.png
40 ...
41 timestamps.txt
42 ...
43 image_07/
44 data/
45 timestamps.txt
46 lidar_points/
47 data/
48 timestamps.txt
49 novatel/
50 data/
51 dataformat.txt
52 timestamps.txt
53 ...
54 0018/
55 calib/
56 00.yaml
57 01.yaml
58 02.yaml
59 03.yaml
60 04.yaml
61 05.yaml
62 06.yaml
63 07.yaml
64 extrinsics.yaml
65 README.txt
66 2018_03_07/
67 2019_02_27/
68
69 Arguments:
70 path: The root directory of the dataset.
71
72 Returns:
73 Loaded `~tensorbay.dataset.dataset.FusionDataset` instance.
74
75 """
76 root_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.expanduser(path))
77
78 dataset = FusionDataset(DATASET_NAME)
79 dataset.notes.is_continuous = True
80 dataset.load_catalog(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "catalog.json"))
81
82 for date in os.listdir(root_path):
83 date_path = os.path.join(root_path, date)
84 sensors = _load_sensors(os.path.join(date_path, "calib"))
85 for index in os.listdir(date_path):
86 if index == "calib":
87 continue
88
89 segment = dataset.create_segment(f"{date}-{index}")
90 segment.sensors = sensors
91 segment_path = os.path.join(root_path, date, index)
92 data_path = os.path.join(segment_path, "labeled")
93
94 with open(os.path.join(segment_path, "3d_ann.json"), "r") as fp:
95 # The first line of the json file is the json body.
96 annotations = json.loads(fp.readline())
97 timestamps = _load_timestamps(sensors, data_path)
98 for frame_index, annotation in enumerate(annotations):
99 segment.append(_load_frame(sensors, data_path, frame_index, annotation, timestamps))
100
101 return dataset
102
103
104def _load_timestamps(sensors: Sensors, data_path: str) -> Dict[str, List[str]]:
105 timestamps = {}
106 for sensor_name in sensors.keys():
107 data_folder = f"image_{sensor_name[-2:]}" if sensor_name != "LIDAR" else "lidar_points"
108 timestamp_file = os.path.join(data_path, data_folder, "timestamps.txt")
109 with open(timestamp_file, "r") as fp:
110 timestamps[sensor_name] = fp.readlines()
111
112 return timestamps
113
114
115def _load_frame(
116 sensors: Sensors,
117 data_path: str,
118 frame_index: int,
119 annotation: Dict[str, Any],
120 timestamps: Dict[str, List[str]],
121) -> Frame:
122 frame = Frame()
123 for sensor_name in sensors.keys():
124 # The data file name is a string of length 10 with each digit being a number:
125 # 0000000000.jpg
126 # 0000000001.bin
127 data_file_name = f"{frame_index:010}"
128
129 # Each line of the timestamps file looks like:
130 # 2018-03-06 15:02:33.000000000
131 timestamp = datetime.strptime(
132 timestamps[sensor_name][frame_index][:23], "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f"
133 ).timestamp()
134 if sensor_name != "LIDAR":
135 # The image folder corresponds to different cameras, whose name is likes "CAM00".
136 # The image folder looks like "image_00".
137 camera_folder = f"image_{sensor_name[-2:]}"
138 image_file = f"{data_file_name}.png"
139
140 data = Data(
141 os.path.join(data_path, camera_folder, "data", image_file),
142 target_remote_path=f"{camera_folder}-{image_file}",
143 timestamp=timestamp,
144 )
145 else:
146 data = Data(
147 os.path.join(data_path, "lidar_points", "data", f"{data_file_name}.bin"),
148 timestamp=timestamp,
149 )
150 data.label.box3d = _load_labels(annotation["cuboids"])
151
152 frame[sensor_name] = data
153 return frame
154
155
156def _load_labels(boxes: List[Dict[str, Any]]) -> List[LabeledBox3D]:
157 labels = []
158 for box in boxes:
159 dimension = box["dimensions"]
160 position = box["position"]
161
162 attributes = box["attributes"]
163 attributes["stationary"] = box["stationary"]
164 attributes["camera_used"] = box["camera_used"]
165 attributes["points_count"] = box["points_count"]
166
167 label = LabeledBox3D(
168 size=(
169 dimension["y"], # The "y" dimension is the width from front to back.
170 dimension["x"], # The "x" dimension is the width from left to right.
171 dimension["z"],
172 ),
173 translation=(
174 position["x"], # "x" axis points to the forward facing direction of the object.
175 position["y"], # "y" axis points to the left direction of the object.
176 position["z"],
177 ),
178 rotation=quaternion.from_rotation_vector((0, 0, box["yaw"])),
179 category=box["label"],
180 attributes=attributes,
181 instance=box["uuid"],
182 )
183 labels.append(label)
184
185 return labels
186
187
188def _load_sensors(calib_path: str) -> Sensors:
189 try:
190 import yaml # pylint: disable=import-outside-toplevel
191 except ModuleNotFoundError as error:
192 raise ModuleImportError(module_name=error.name, package_name="pyyaml") from error
193
194 sensors = Sensors()
195
196 lidar = Lidar("LIDAR")
197 lidar.set_extrinsics()
198 sensors.add(lidar)
199
200 with open(os.path.join(calib_path, "extrinsics.yaml"), "r") as fp:
201 extrinsics = yaml.load(fp, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
202
203 for camera_calibration_file in glob(os.path.join(calib_path, "[0-9]*.yaml")):
204 with open(camera_calibration_file, "r") as fp:
205 camera_calibration = yaml.load(fp, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
206
207 # camera_calibration_file looks like:
208 # /path-to-CADC/2018_03_06/calib/00.yaml
209 camera_name = f"CAM{os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(camera_calibration_file))[0]}"
210 camera = Camera(camera_name)
211 camera.description = camera_calibration["camera_name"]
212
213 camera.set_extrinsics(matrix=extrinsics[f"T_LIDAR_{camera_name}"])
214
215 camera_matrix = camera_calibration["camera_matrix"]["data"]
216 camera.set_camera_matrix(matrix=[camera_matrix[:3], camera_matrix[3:6], camera_matrix[6:9]])
217
218 distortion = camera_calibration["distortion_coefficients"]["data"]
219 camera.set_distortion_coefficients(**dict(zip(("k1", "k2", "p1", "p2", "k3"), distortion)))
220
221 sensors.add(camera)
222 return sensors
create a fusion dataset
To load a fusion dataset, we first need to create an instance of FusionDataset.(L75)
Note that after creating the fusion dataset,
you need to set the is_continuous attribute of notes to True,(L76)
since the frames
in each fusion segment is time-continuous.
load the catalog
Same as dataset, you also need to load the catalog.(L77) The catalog file “catalog.json” is in the same directory with dataloader file.
create fusion segments
In this example, we create fusion segments by dataset.create_segment(SEGMENT_NAME).(L86)
We manage the data under the subfolder(L33) of the date folder(L32) into a fusion segment
and combine two folder names to form a segment name,
which is to ensure that frames in each segment are continuous.
add sensors to fusion segments
After constructing the fusion segment, the sensors corresponding to different data should be added to the fusion segment.(L87)
In “CADC” , there is a need for projection, so we need not only the name for each sensor, but also the calibration parameters.
And to manage all the Sensors (L81, L183) corresponding to different data,
the parameters from calibration files are extracted.
Lidar sensor only has extrinsics,
here we regard the lidar as the origin of the point cloud 3D coordinate system, and set the extrinsics as defaults(L189).
To keep the projection relationship between sensors,
we set the transform from the camera 3D coordinate system to the lidar 3D coordinate system
as Camera extrinsics(L205).
Besides extrinsics(),
Camera sensor also has intrinsics(),
which are used to project 3D points to 2D pixels.
The intrinsics consist of two parts,
CameraMatrix and DistortionCoefficients.(L208-L211)
add frames to segment
After adding the sensors to the fusion segments, the frames should be added into the continuous segment in order(L96).
Each frame contains the data corresponding to each sensor, and each data should be added to the frame under the key of sensor name(L147).
In fusion datasets, it is common that not all data have labels. In “CADC”, only point cloud files(Lidar data) have Box3D type of labels(L145). See this page for more details about Box3D annotation details.
Note
The CADC dataloader above uses relative import(L16-L19). However, when you write your own dataloader you should use regular import. And when you want to contribute your own dataloader, remember to use relative import.
Visualize Dataset
Optionally, the organized dataset can be visualized by Pharos, which is a TensorBay SDK plug-in. This step can help users to check whether the dataset is correctly organized. Please see Visualization for more details.
Upload Fusion Dataset
After you finish the dataloader and organize the “CADC” into a
FusionDataset instance, you can upload it
to TensorBay for sharing, reuse, etc.
# fusion_dataset is the one you initialized in "Organize Fusion Dataset" section
fusion_dataset_client = gas.upload_dataset(fusion_dataset, jobs=8)
fusion_dataset_client.commit("initial commit")
Remember to execute the commit step after uploading. If needed, you can re-upload and commit again. Please see this page for more details about version control.
Note
Commit operation can also be done on our GAS Platform.
Read Fusion Dataset
Now you can read “CADC” dataset from TensorBay.
fusion_dataset = FusionDataset("CADC", gas)
In dataset “CADC”, there are lots of
FusionSegments: 2018_03_06/0001, 2018_03_07/0001, …
You can get the segment names by list them all.
fusion_dataset.keys()
You can get a segment by passing the required segment name.
fusion_segment = fusion_dataset["2018_03_06/0001"]
Note
If the segment or fusion segment is created without given name, then its name will be “”.
In the 2018_03_06/0001 fusion segment,
there are several sensors.
You can get all the sensors by accessing the sensors
of the FusionSegment.
sensors = fusion_segment.sensors
In each fusion segment, there are a sequence of frames. You can get one by index.
frame = fusion_segment[0]
In each frame, there are several data corresponding to different sensors. You can get each data by the corresponding sensor name.
for sensor_name in sensors.keys():
data = frame[sensor_name]
In “CADC”, only data
under Lidar
has a sequence of Box3D annotations.
You can get one by index.
lidar_data = frame["LIDAR"]
label_box3d = lidar_data.label.box3d[0]
category = label_box3d.category
attributes = label_box3d.attributes
There is only one label type in “CADC” dataset, which is box3d.
The information stored in category is
one of the category names in “categories” list of catalog.json.
The information stored in attributes
is some of the attributes in “attributes” list of catalog.json.
See this page for more details about the structure of Box3D.
Delete Fusion Dataset
To delete “CADC”, run the following code:
gas.delete_dataset("CADC")